What——什么是容器
容器由两部分组成:(1)应用程序本身;(2)依赖:比如应用程序需要的库或其他软件容器在Host操作系统的用户空间中运行,与操作系统的其他进程隔离。这一点显著区别于的虚拟机。
传统的虚拟化技术,比如VMWare、KVM、Xen,目标是创建完整的虚拟机。为了运行应用,除了部署应用本身及其依赖(通常几十MB),还得安装整个操作系统(几十GB)。
Why——为什么需要容器
容器使软件具备了超强的可移植能力。
这篇文章有一张思维导图足以
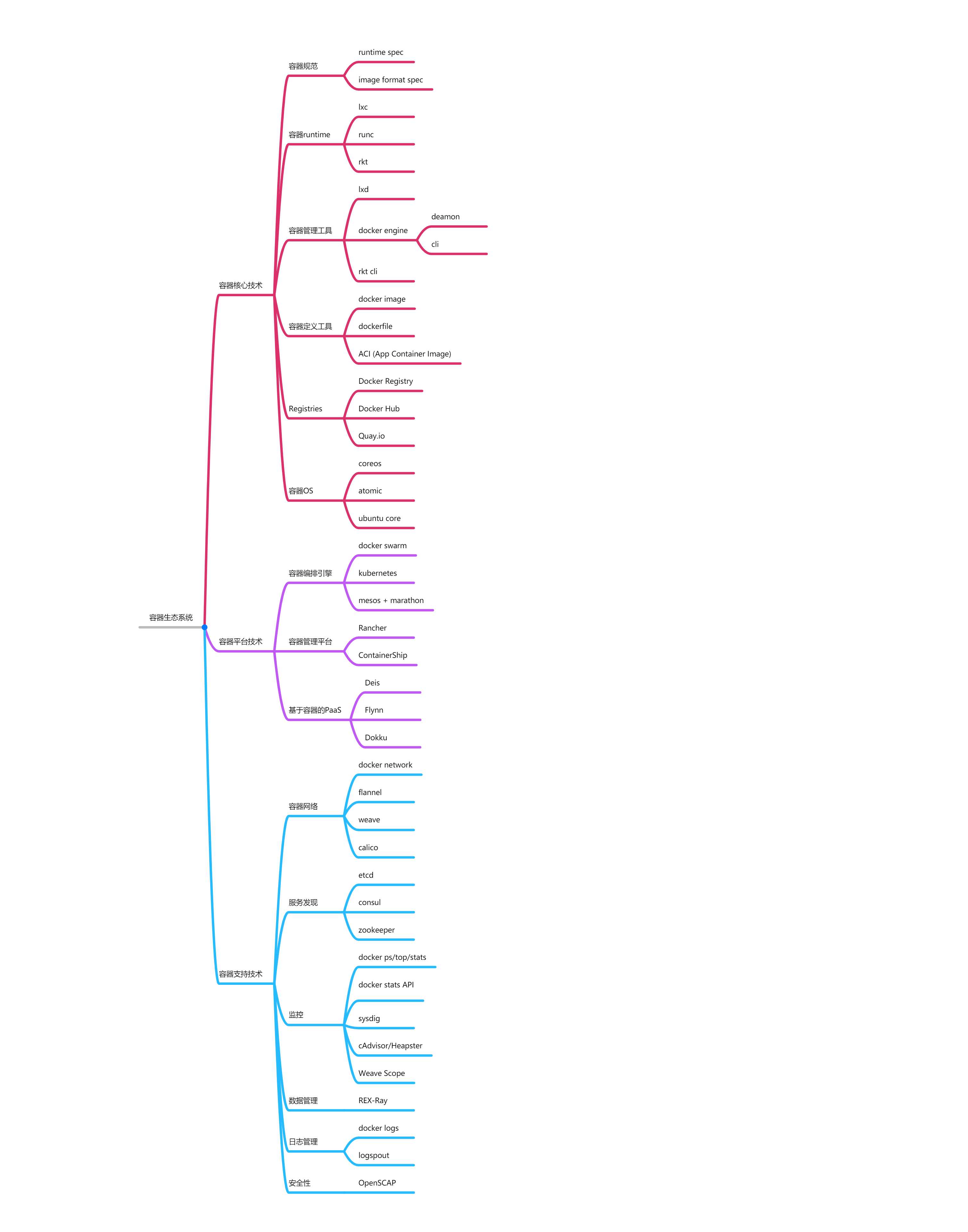
意外发现一本国人写的《玩转Docker容器技术》,好好学习一下Docker系列,就从开头为fun with...开始。
三月到来,各个企业又开始招人了,我也收到了几家企业的面试邀请。
找工作避免不了被问到“是否接受加班?”————当然是看情况了,我有事就拒绝加班,没事但是一天的工作没做完肯定是会自觉加班的,但我最讨厌最讨厌最讨厌那种磨洋工式的加班。
今天就收到了一位很有礼貌的猎头小哥问我“有家游戏公司995可以接受吗?” 我果断拒绝,因为说是995,有可能就临上线就变成996甚至997,人的欲望是无穷无尽的,所以如何摆脱困境,就是要找到从根源上就拒绝加班的企业。
犹记得我在第一家游戏公司的时候,美其名曰加班,实际上是因为一个人回去也没啥意思,就跟着同事一块在公司看书学习敲代码,顺便拿加班补贴和打车补助;第二家公司,刚开始基本7点就准时下班了,但后面逐渐开始那种毫无意义的加班,甚至根据加班来看工作态度、年终考核的时候,我放弃了,放弃了那可有可无的年终奖。
因此,我看透了国内这种加班的本质,要么高效完成工作,要么加班按照劳动法给加班费,否则一切强制无意义的加班就是压榨。
花了将近一个月终于刷完了算法训练营,让我系统学习了算法与数据结构的知识,尤其是后面接触的字典树、并查集、布隆过滤器、AVL Tree、红黑树这种高级数据结构,让我不得不感人类思想的伟大。
字符串算法和排序算法很重要,面试经常考,要及时掌握,同时不能放弃刷题,要时刻保持做题手感,同时要时刻借鉴别人优秀的解题思路。这样编程能力以及算法的基本功会慢慢得到提升。
加油!^_^
GATC
时间复杂度和空间复杂度分析
数组、链表、跳表
树、二叉树、二叉搜索树
递归
算法体验营-结课考试题
栈和队列
动态规划
Trie树、并查集
位运算基础
哈希表、映射、集合
分治、回溯
深度优先搜索、广度优先搜索
贪心算法
二分查找
初级排序和高级排序
字符串基础知识、高级字符串算法、字符串匹配算法
高级搜索
AVL树和红黑树
布隆过滤器、LRUCache
动态规划、状态转移方程