题目
力扣-剑指 Offer 07. 重建二叉树
知识点
1,前序(Pre-order):根-左-右
2,中序(In-order):左-根-右
3,后序(Post-order):左-右-根
题解
解法一:递归
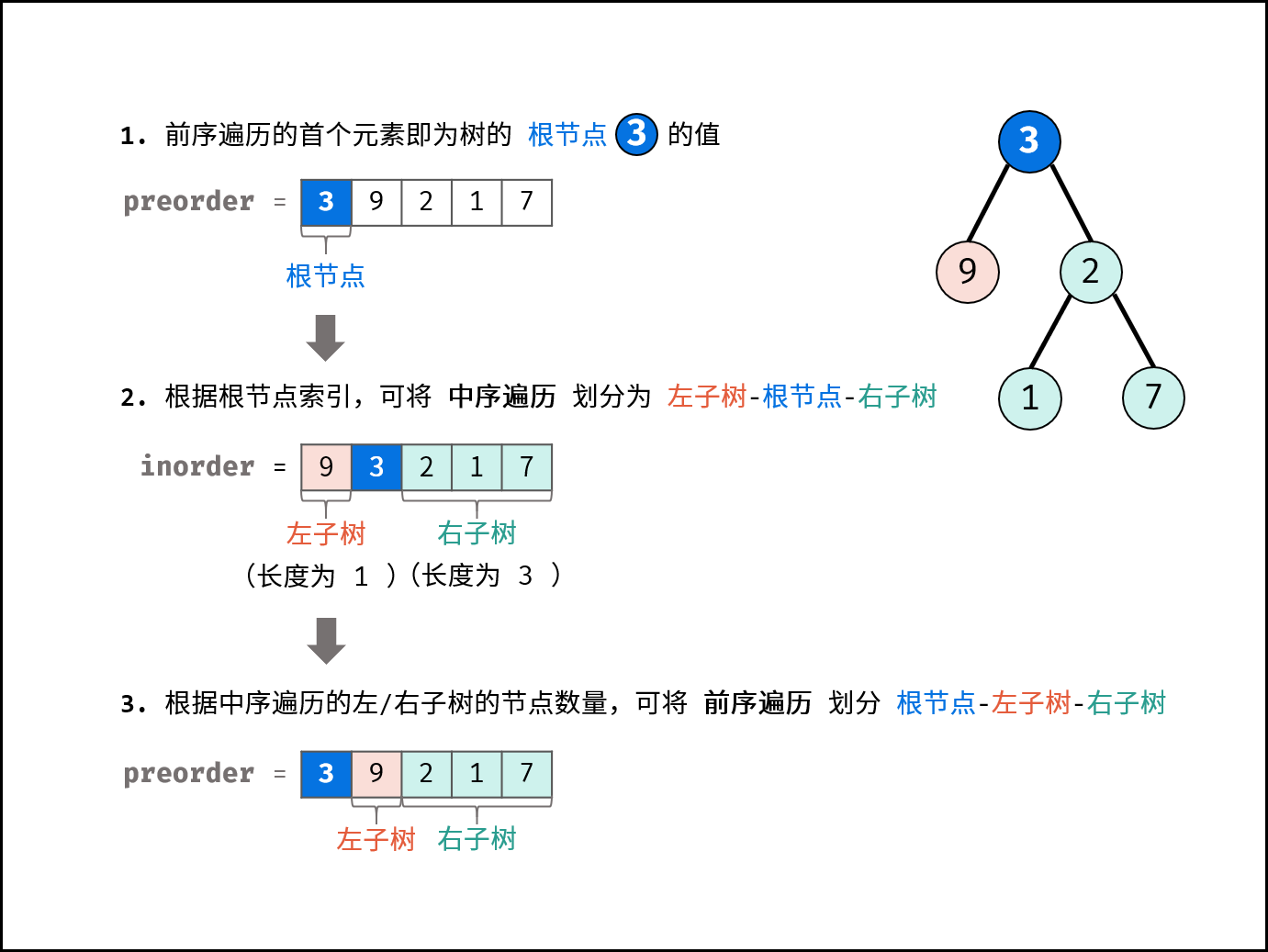
按题目给的示例来划分:
前序遍历划分 [ 3 | 9 | 20 15 7 ]
中序遍历划分 [ 9 | 3 | 15 20 7 ]
根据以上性质,可得出以下推论:
- 前序遍历的首元素 为 树的根节点
node 的值。
- 在中序遍历中搜索根节点
node 的索引 ,可将 中序遍历 划分为 [ 左子树 | 根节点 | 右子树 ] 。
- 根据中序遍历中的左 / 右子树的节点数量,可将 前序遍历 划分为 [ 根节点 | 左子树 | 右子树 ] 。
考虑通过递归对所有子树进行划分:
递推参数: 根节点在前序遍历的索引 root 、子树在中序遍历的左边界 left 、子树在中序遍历的右边界 right ;
终止条件: 当 left > right ,代表已经越过叶节点,此时返回 null ;
递推工作:
建立根节点 node : 节点值为 preorder[root] ;
划分左右子树: 查找根节点在中序遍历 inorder 中的索引 i ;
网上摘的保姆式的注解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
|
class Solution {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int[] preorder;
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
this.preorder = preorder;
for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) {
map.put(inorder[i], i);
}
return recur(0,0,inorder.length-1);
}
TreeNode recur(int pre_root, int in_left, int in_right){
if(in_left > in_right) return null;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[pre_root]);
int idx = map.get(preorder[pre_root]);
root.left = recur(pre_root+1, in_left, idx-1);
root.right = recur(pre_root + (idx - in_left) + 1, idx+1, in_right);
return root;
}
}
|
leetcode-cn执行:
1
2
3
4
| 执行用时:
3 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了55.11%的用户
内存消耗:
38.4 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了80.00%的用户
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
func buildTree(preorder []int, inorder []int) *TreeNode {
root := new(TreeNode)
if len(preorder) == 0 {
return nil
}
root_val := preorder[0]
i := 0
for inorder[i] != root_val {
i++
}
left_tree := buildTree(preorder[1:i+1],inorder[:i])
right_tree := buildTree(preorder[i+1:],inorder[i+1:])
root.Val = root_val
root.Left = left_tree
root.Right = right_tree
return root
}
|
leetcode-cn执行:
1
2
3
4
| 执行用时:
4 ms, 在所有 Go 提交中击败了95.75%的用户
内存消耗:
4.2 MB, 在所有 Go 提交中击败了25.36%的用户
|
牛客网运行:
1
2
3
4
| 运行时间:5ms
超过39.31%用Go提交的代码
占用内存:2344KB
超过9.75%用Go提交的代码
|
思考:为什么二叉树的题目一般用递归来解?
参考链接
4种解法(递归,栈,队列),最后一种击败了100%的用户
力扣官方题解
【面试题】重建二叉树(解题思路分析+Java、Python实现+代码详细注释)
面试题07. 重建二叉树(递归法,清晰图解)


