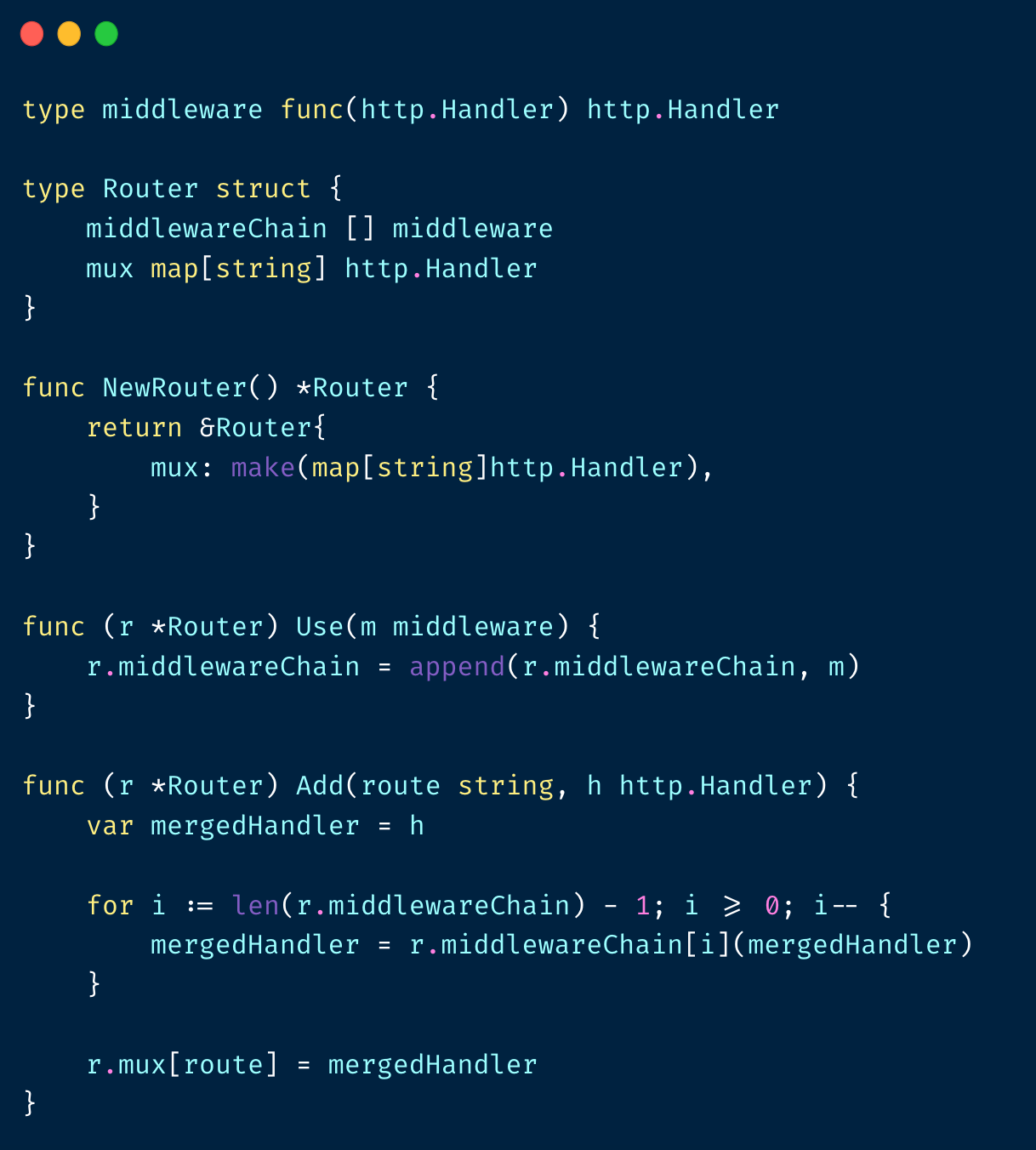
middleware 实现
middleware/filter 实现
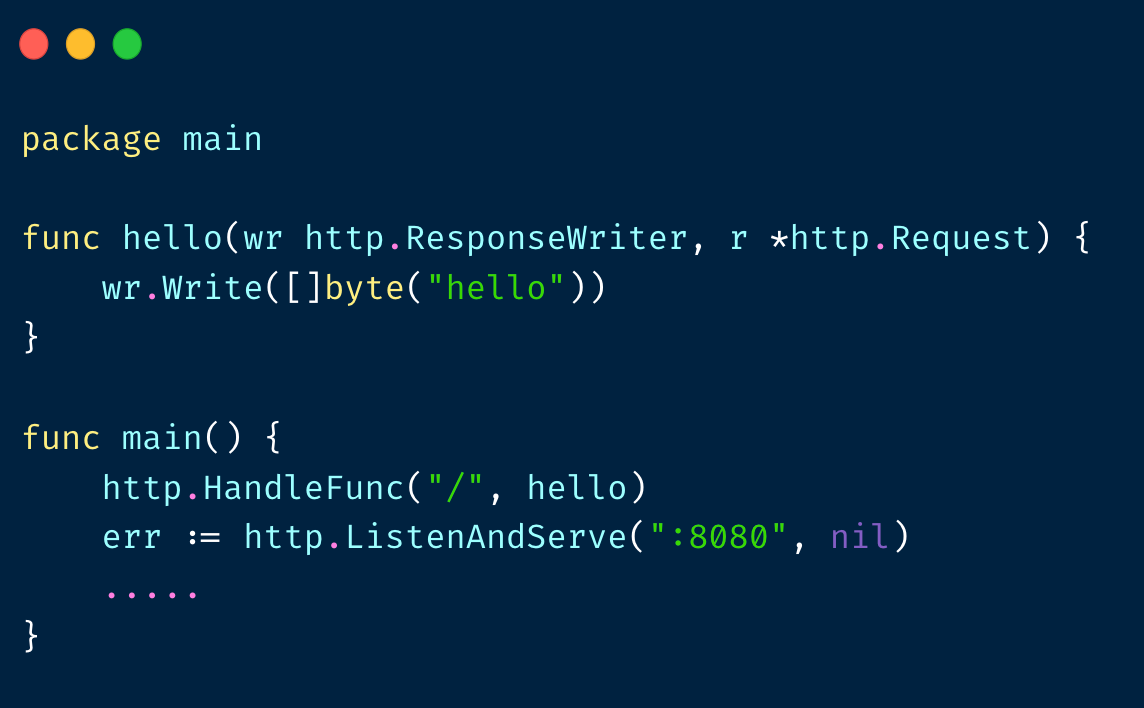
我们有这样⼀个 hello world 的业务逻辑:
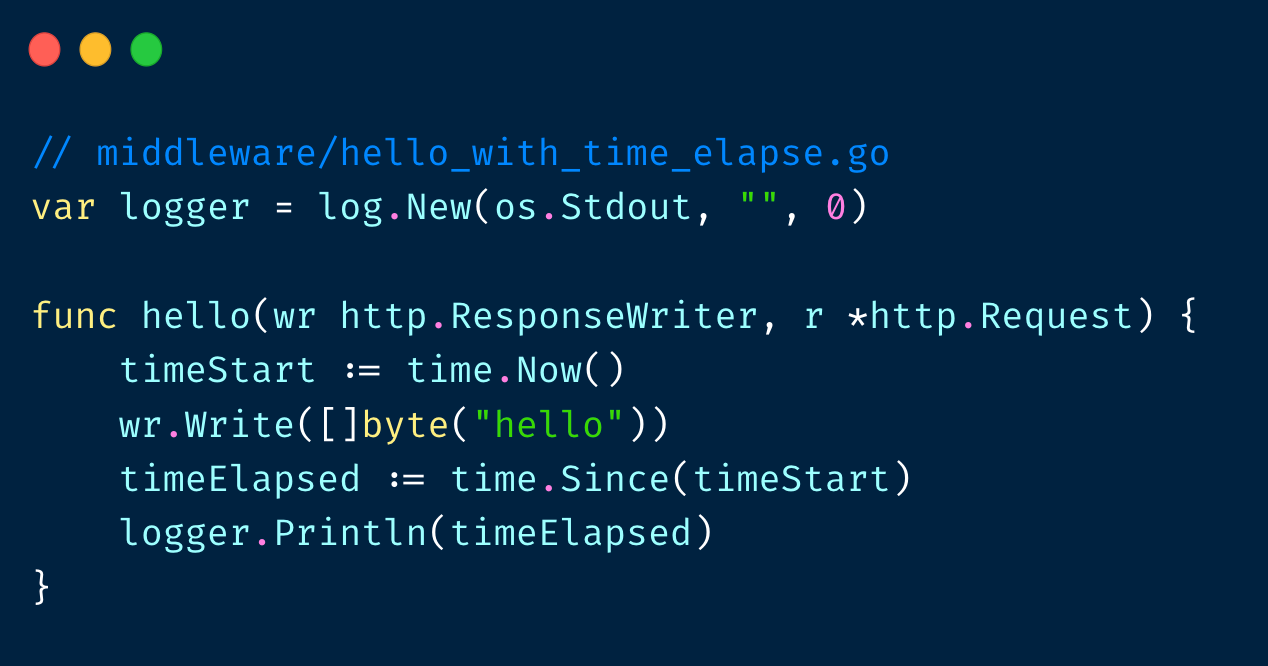
如果想要统计每个请求花的时间:
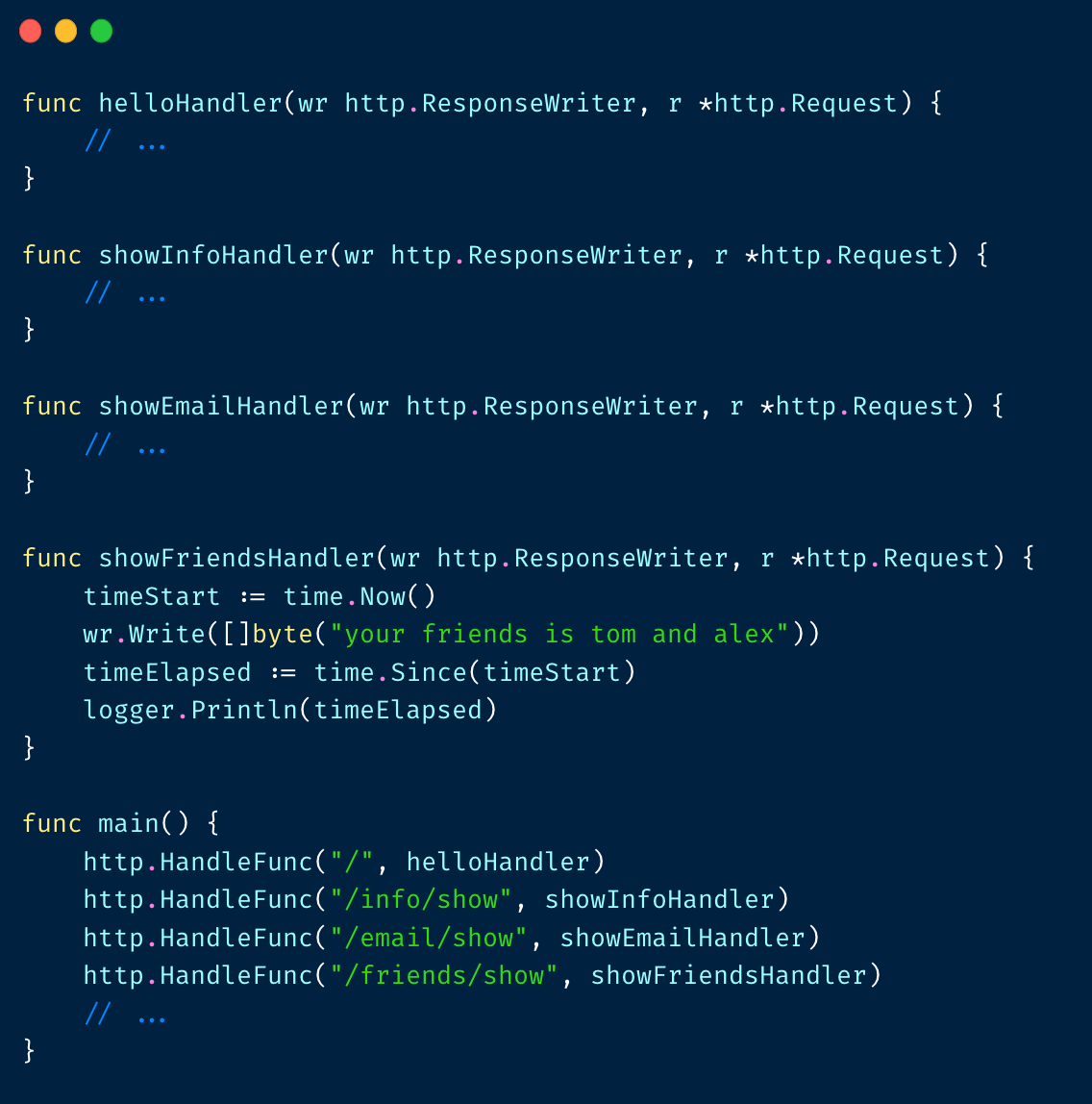
随着业务的迭代,接⼝会逐渐增加:
公司发展壮⼤后,我们希望能把耗时可视化:

基本思路是,把功能性(业务代码)和⾮功能性(⾮业务代码)分离
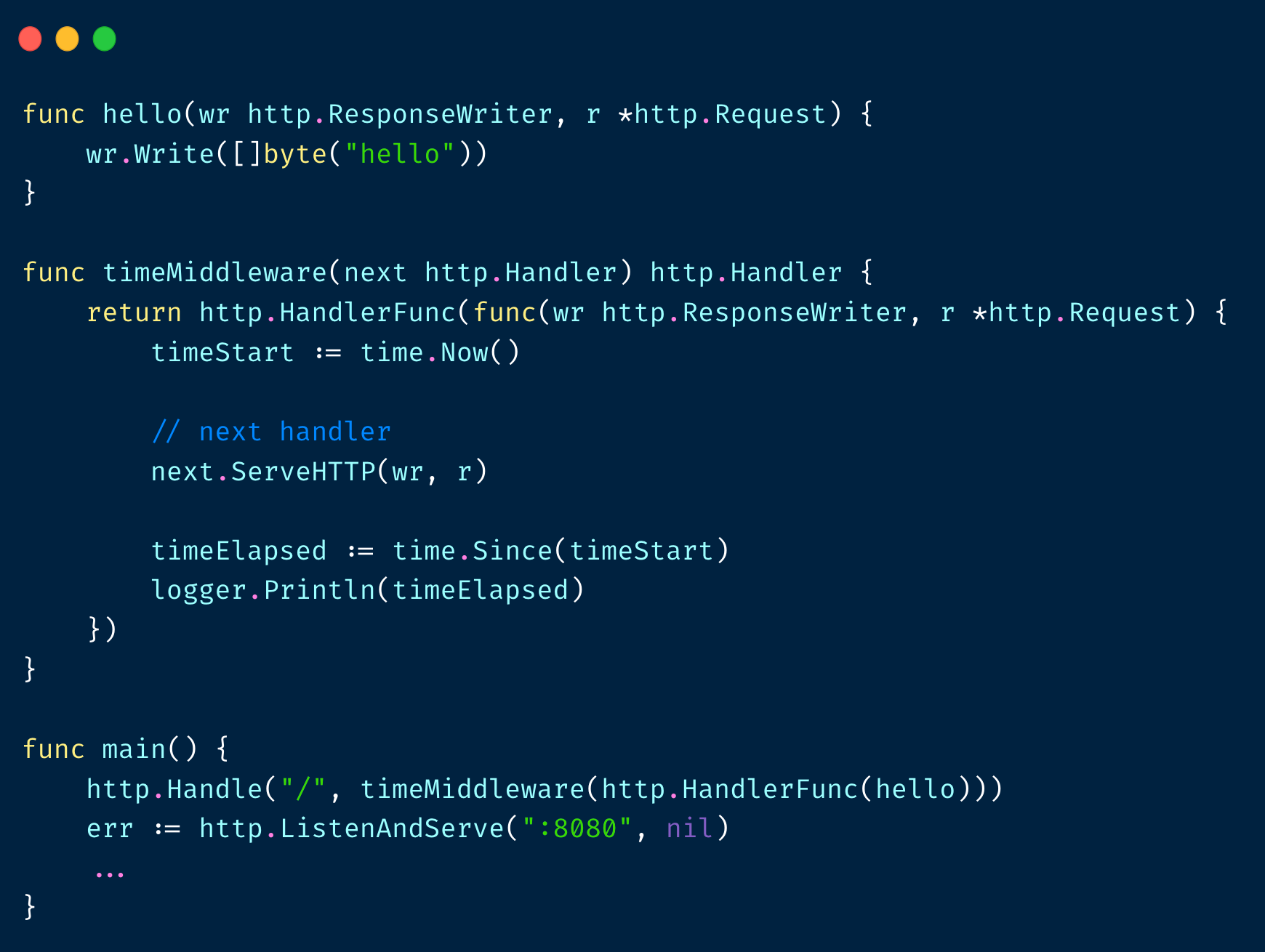

- 和 HandlerFunc 有相同签名的函数可以强制转换为 HandlerFunc
- HandlerFunc 实现了 ServeHTTP ⽅法,所以 HandlerFunc 实现了 http.Handler 接⼝

多个中间件⼀般这么写就好了
不过这样写很丑,一般这样写:

实现也很简单:
⼀个 http 的请求处理过程:
![])(./go-senior-engineer-8-in-depth-web-framework-principle-and-realization/http.png)
常⻅ middleware
https://github.com/gin-gonic/contrib
router 实现
Router 本质
![])(./go-senior-engineer-8-in-depth-web-framework-principle-and-realization/rt.png)
字典树 trie
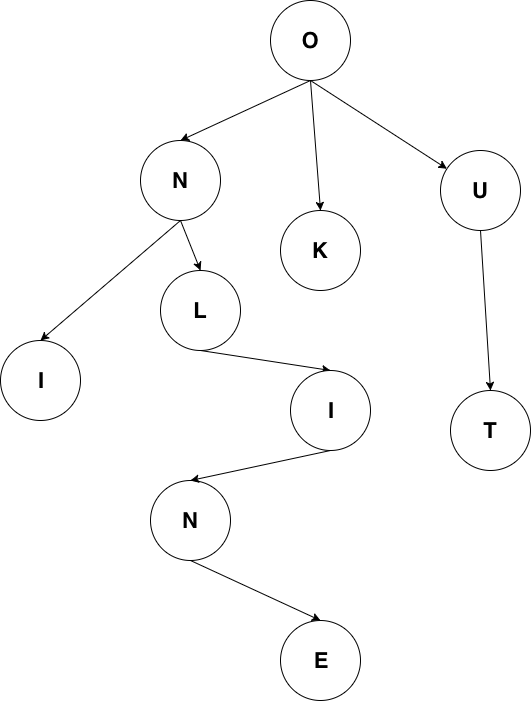
- 单个节点代表⼀个字⺟
- 如果需要对字符串进⾏匹配
- 只要从根节点开始依次匹配即可
Radix Tree
In computer science, a radix tree (also radix trie or compact prefix tree) is a data structure that represents a space-optimized trie (prefix tree) in which each node that is the only child is merged with its parent. The result is that the number of children of every internal node is at most the radix r of the radix tree, where r is a positive integer and a power x of 2, having x ≥ 1. Unlike regular trees, edges can be labeled with sequences of elements as well as single elements. This makes radix trees much more efficient for small sets (especially if the strings are long) and for sets of strings that share long prefixes.
同⼀个 URI 在 HTTP 规范中会有多个⽅法
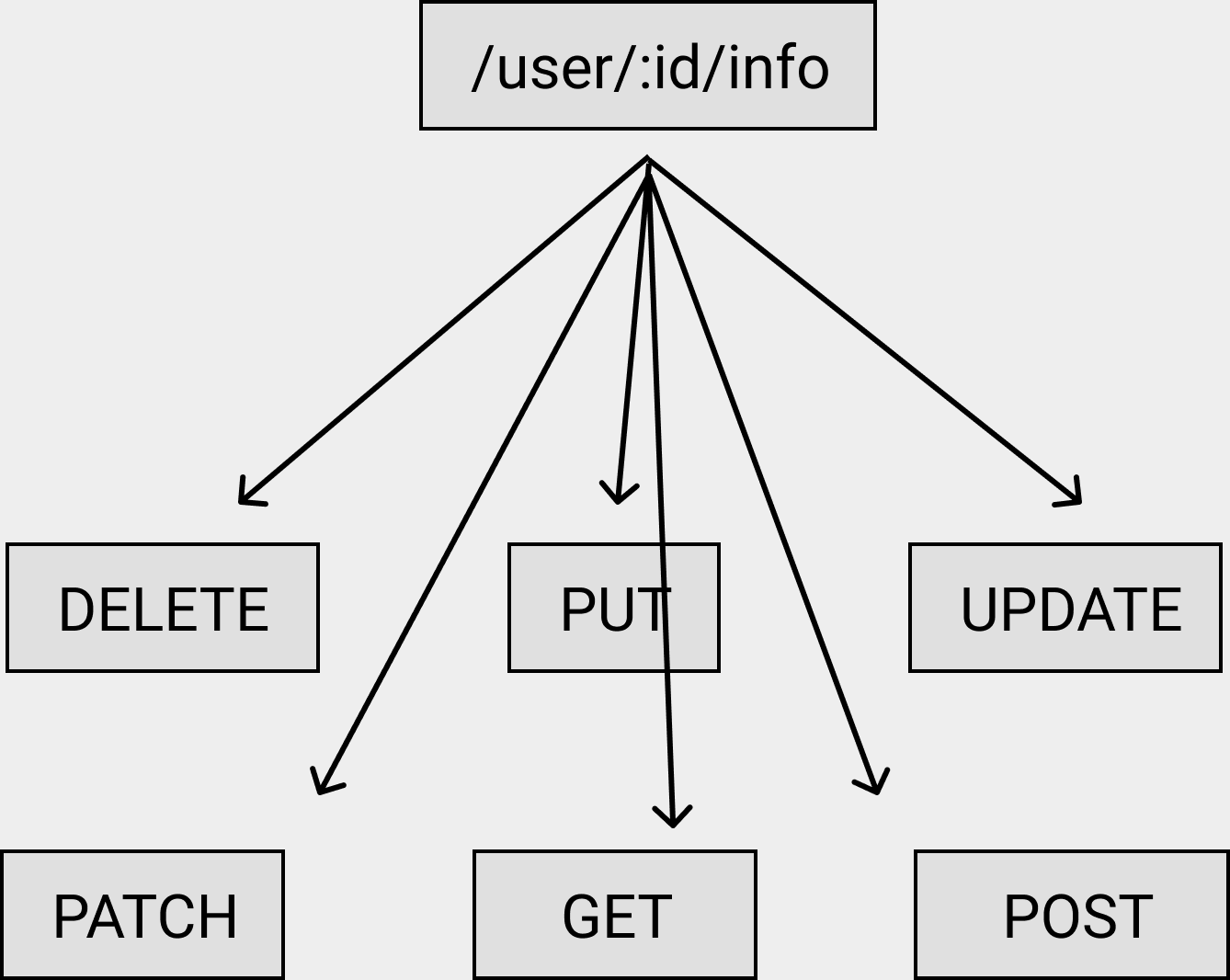
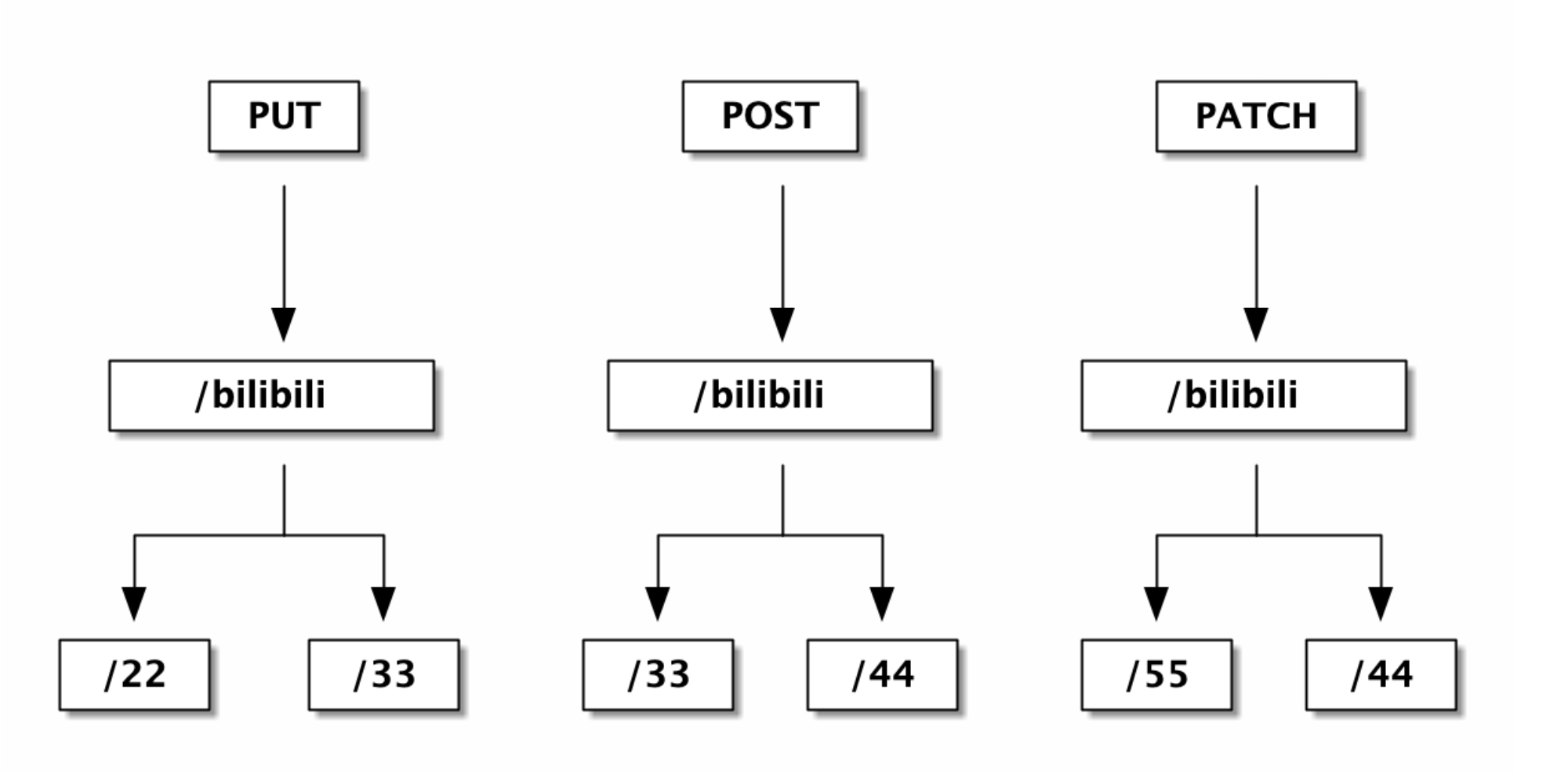
每⼀个 method 对应⼀棵 radix tree:
httprouter 实现细节
node
就是 httprouter 树中的节点。
nType
就是 node type,有⼏种枚举值:
1 | • static // ⾮根节点的普通字符串节点 |
path
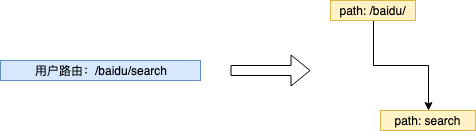
到达节点时,所经过的字符串路径
indices
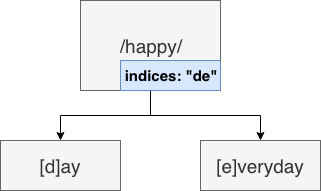
⼦节点索引,当⼦节点为⾮参数类型,即本节点的 wildChild 为 false时,会将每个⼦节点的⾸字⺟放在该索引数组。说是数组,实际上是个string。
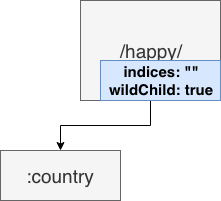
如果⼦节点为参数节点时,indices 应该是个空字符串。
wildChild
如果⼀个节点的⼦节点中有 param(wildcard) 节点,那么该节点的 wildChild 字段即为 true。
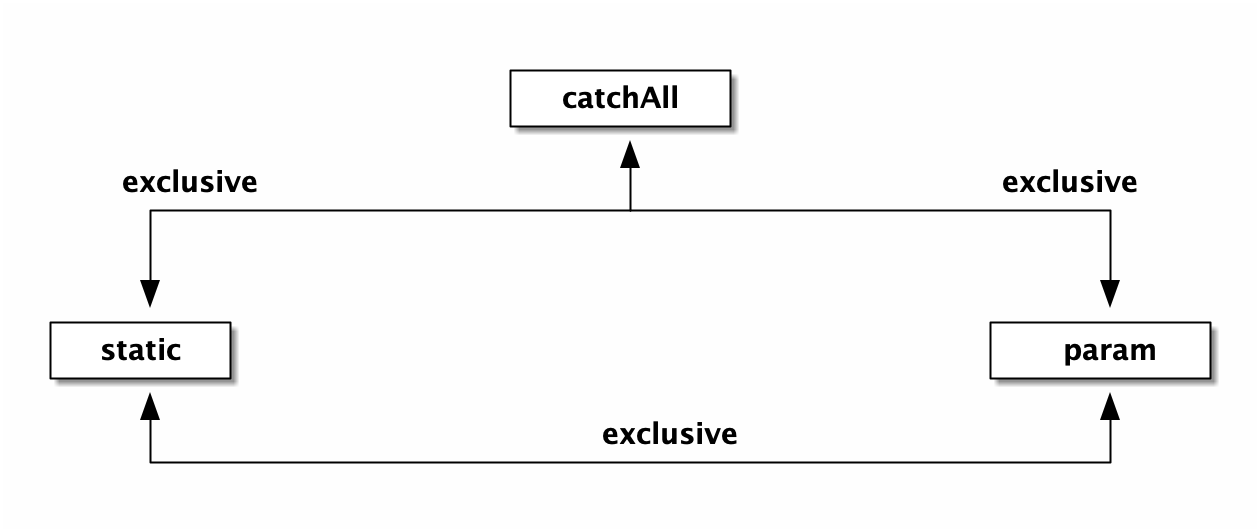
catchAll
以 * 结尾的路由,即为 catchAll。在静态⽂件服务上,catchAll ⽤的⽐较多。后⾯的部分⼀般⽤来描述⽂件路径。如:/software/downloads/monodraw-latest.dmg。
Radix Tree 的构造过程
第⼀条路由
插⼊ /marketplace_listing/plans/
第⼆条路由
插⼊ /marketplace_listing/plans/:id/acounts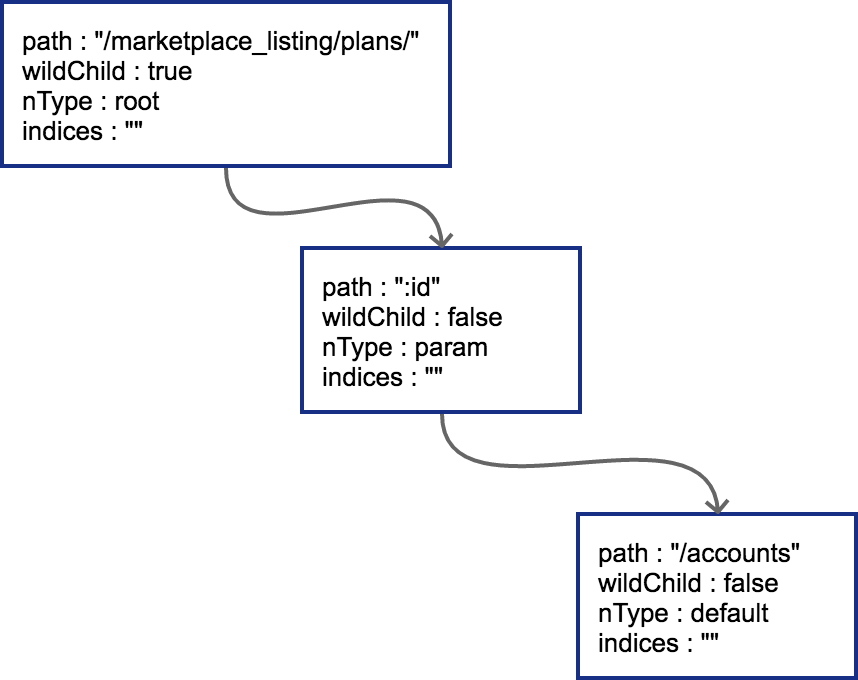
第三条路由
插⼊ /search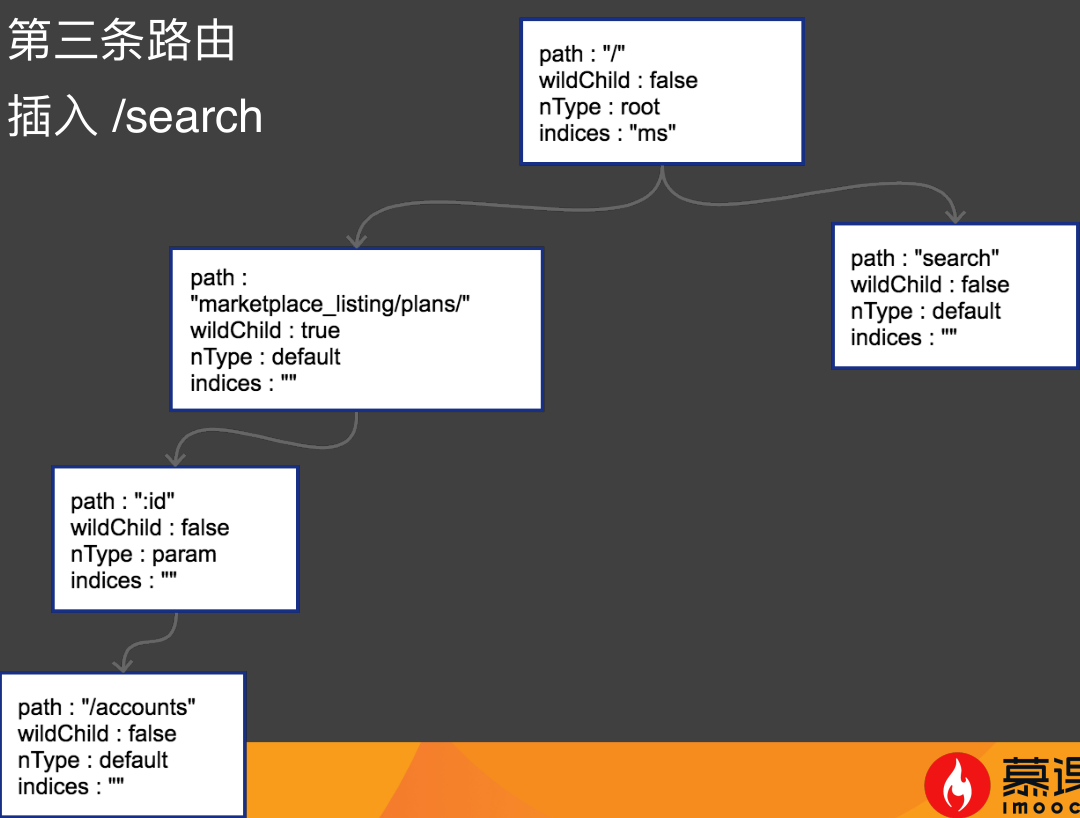
路由冲突
conflict:
GET /user/info/:name
GET /user/:id
no conflict:
GET /user/info/:name
POST /user/:id
路由冲突细则
- 在插⼊ wildcard 节点时,⽗节点的 children 数组⾮空且 wildChild 被设置为 false。
例如:GET /user/getAll 和 GET /user/:id/getAddr,或者 GET /user/*aaa和 GET /user/:id。 - 在插⼊ wildcard 节点时,⽗节点的 children 数组⾮空且 wildChild 被设置为 true,但该⽗节点的 wildcard ⼦节点要插⼊的 wildcard 名字不⼀样。
例如: GET /user/:id/info 和 GET /user/:name/info。 - 在插⼊ catchAll 节点时,⽗节点的 children ⾮空。
例如: GET /src/abc和 GET /src/*filename,或者 GET /src/:id 和 GET /src/*filename。 - 在插⼊ static 节点时,⽗节点的 wildChild 字段被设置为 true。 在插⼊static 节点时,⽗节点的 children ⾮空,且⼦节点 nType 为 catchAll。

validator 实现
为什么需要 validator
看看这坨代码: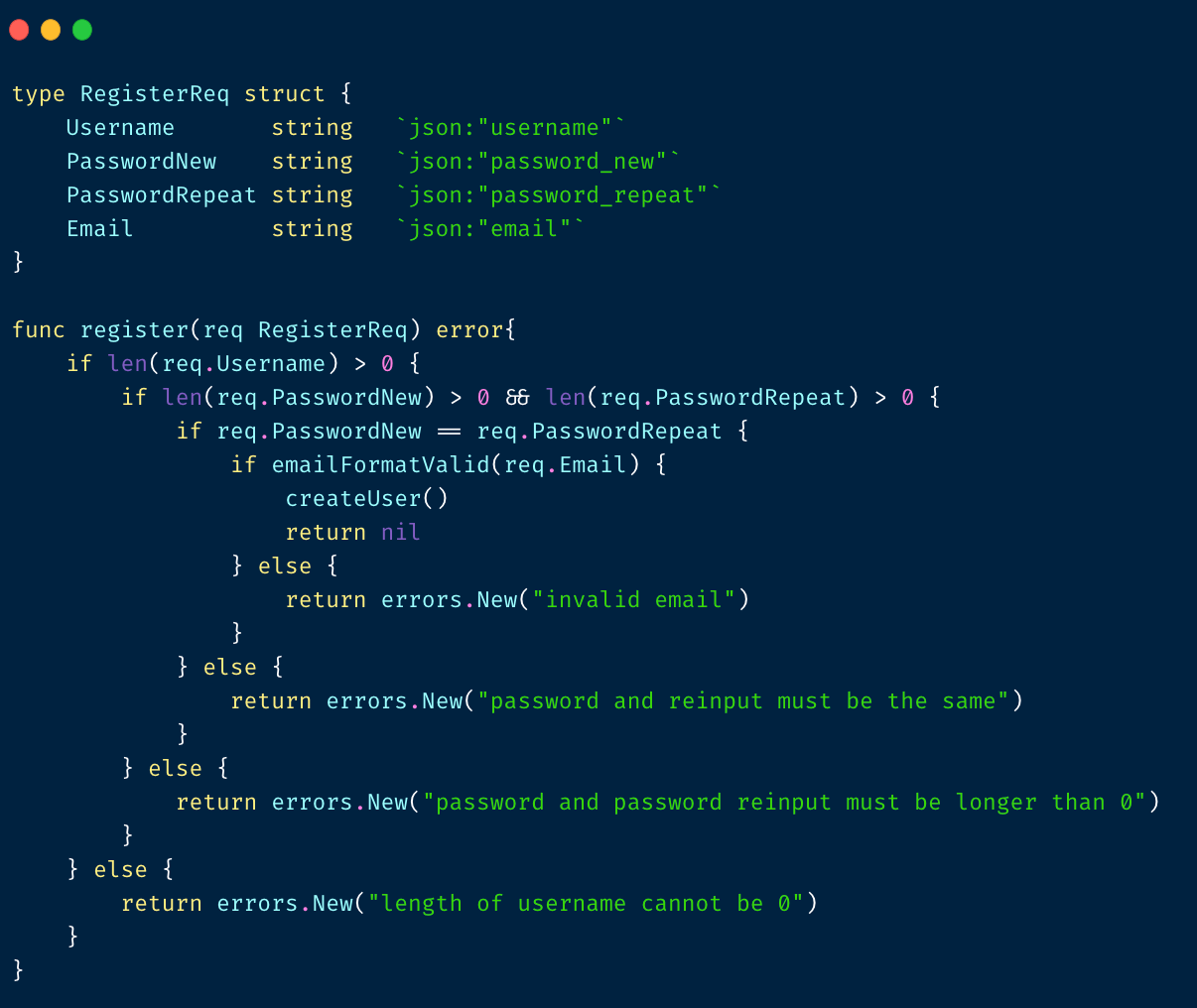
使⽤ early return/guard clause 重构之后,代码还是太丑: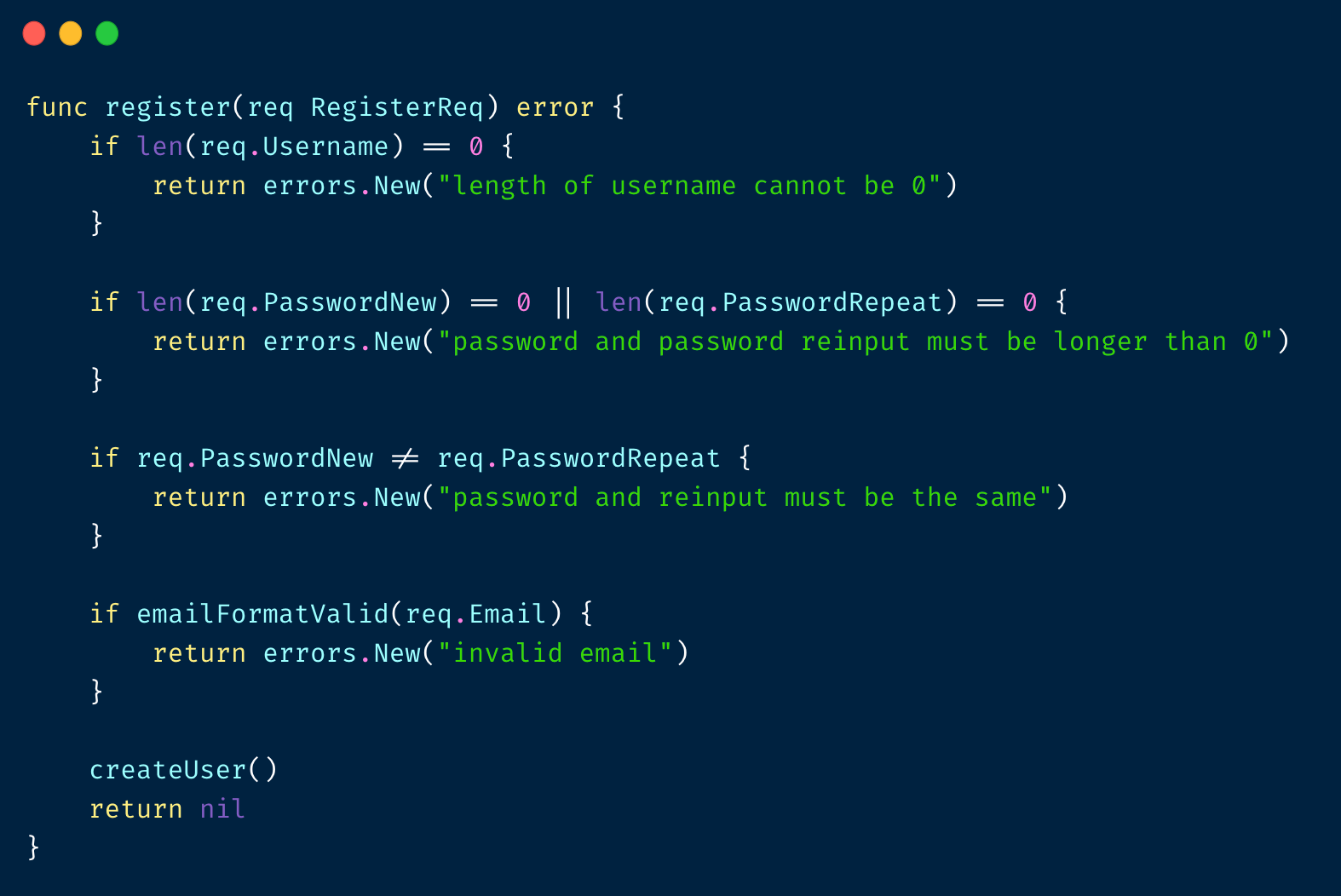
validator 改造: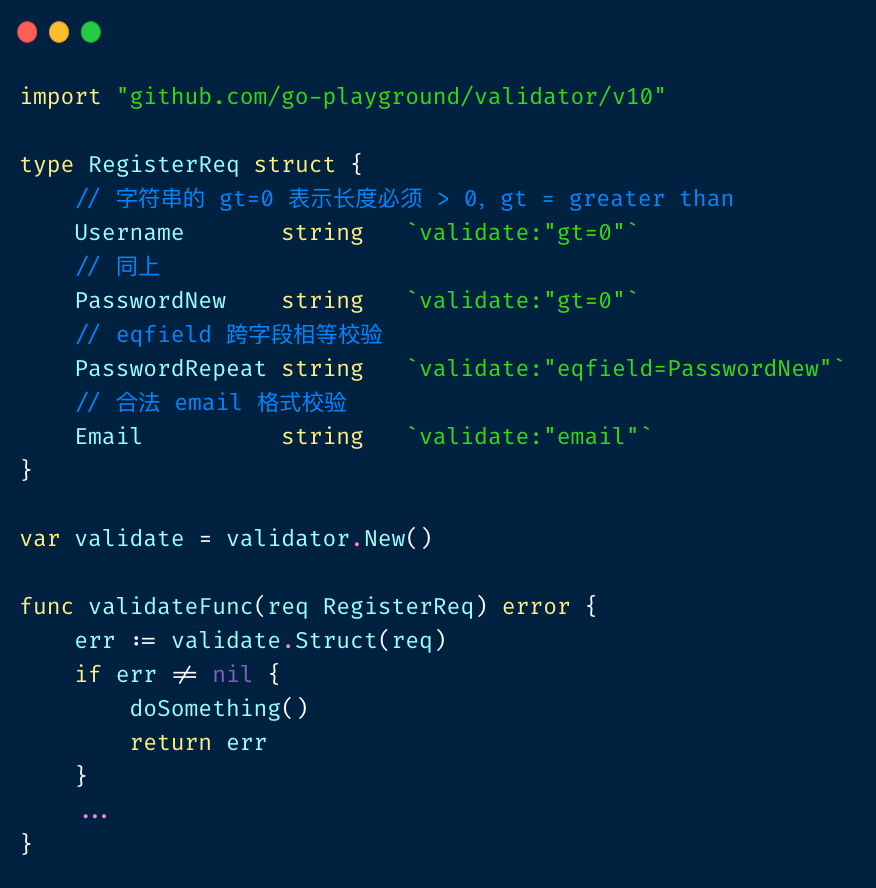
validator 基本原理
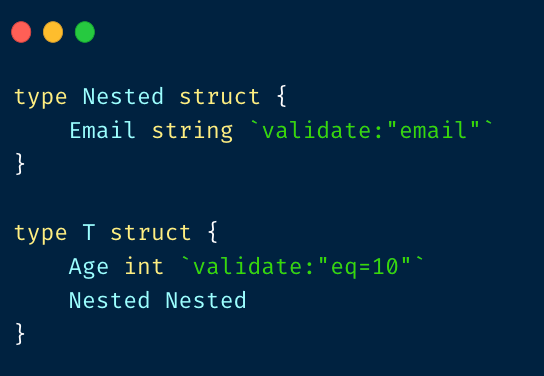
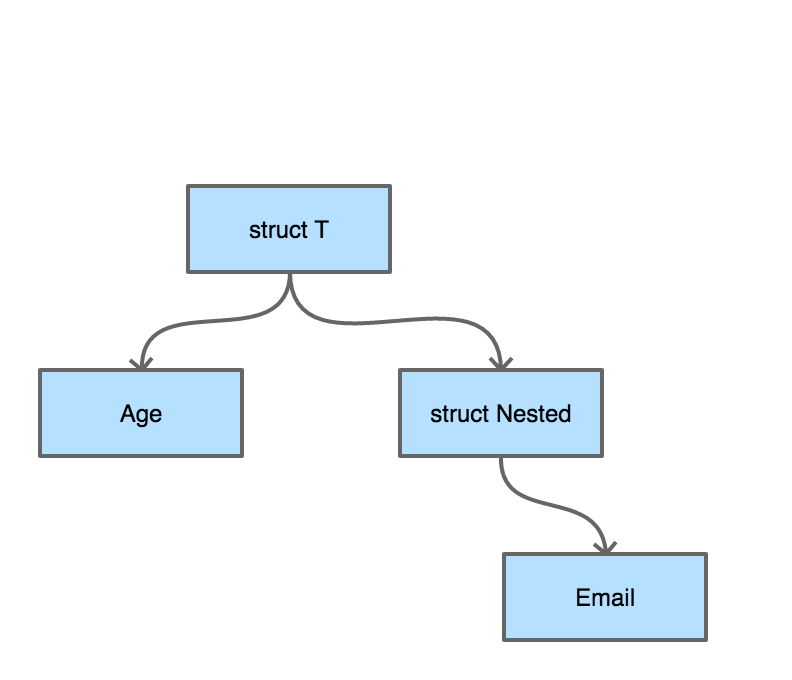
request binder 实现
Gin 的 binding
HTTP header : Content-Type

不同的⼯⼚实现很简单,就是某种 codec 的 unmarshal
sql binder 实现
标准库的 API 难⽤
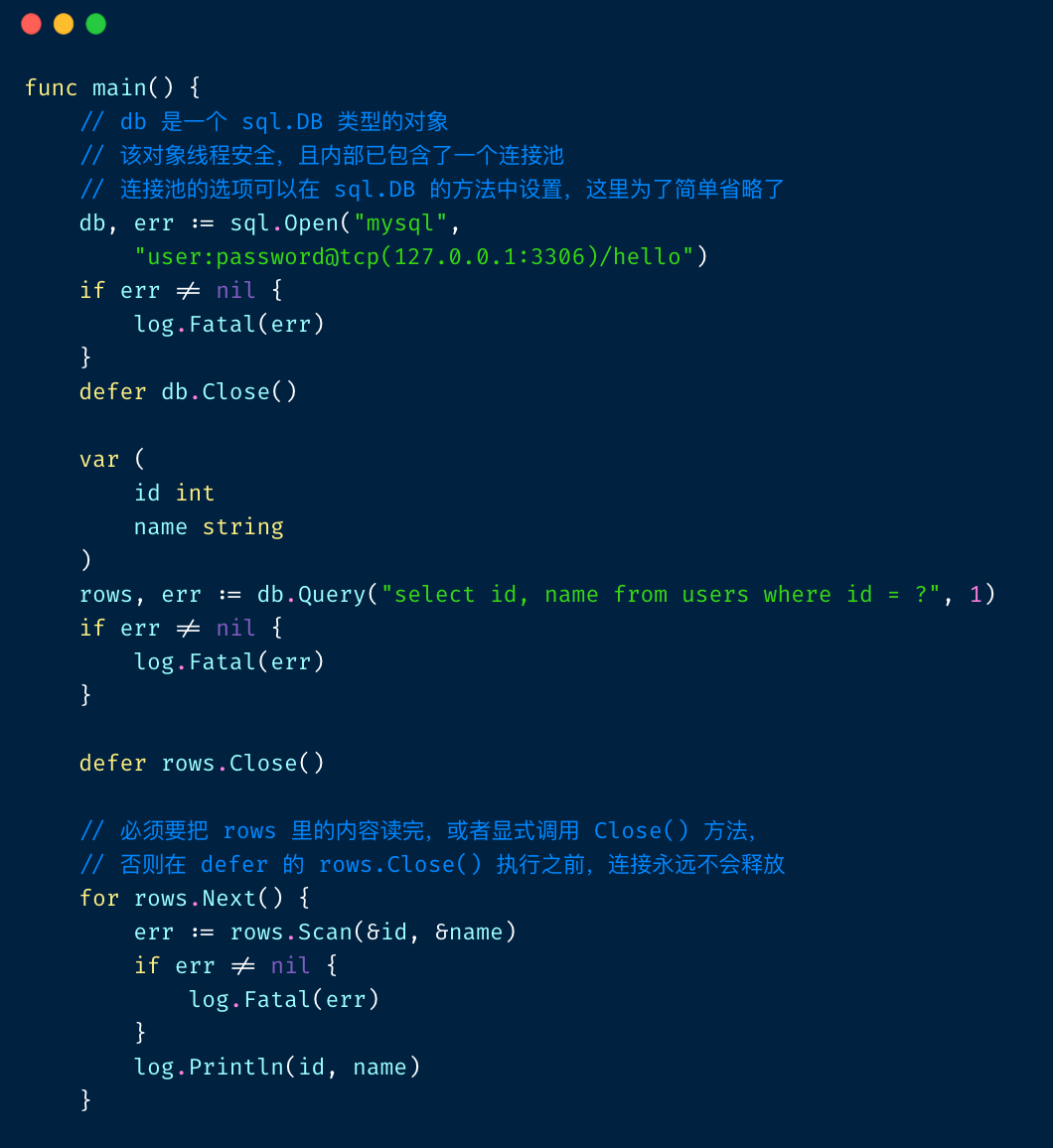
- 标准库的 API 难⽤且容易犯错
- 有⽆数的新⼿ Gopher 倒在 sql.Rows 忘记关闭的坑下
SQL binder 实现
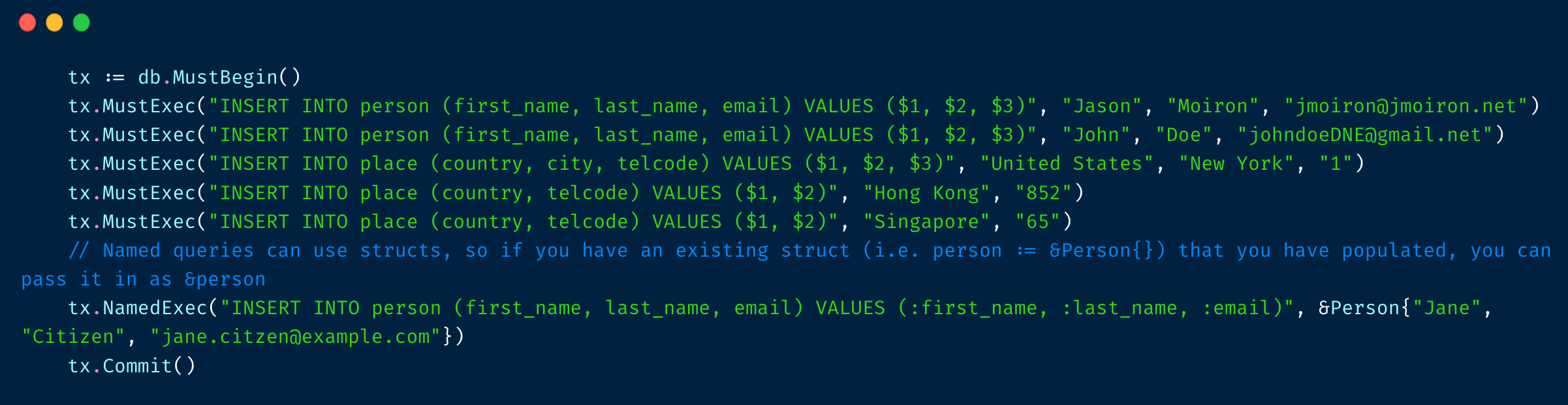
实现很简单,只要能把特殊开头的单词提取出来就可以了,⽐如:开头,@开头,$开头。
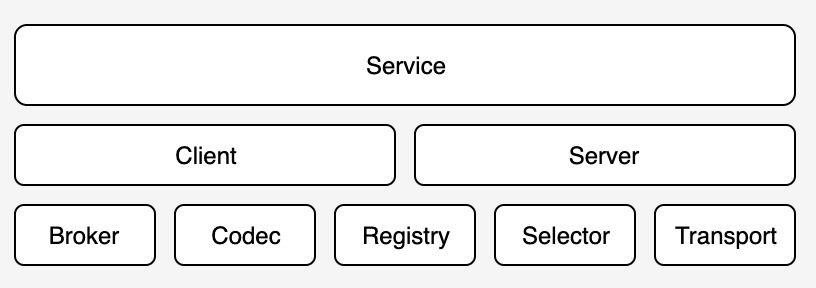
go-micro 实现
插件化原理:
References
维基百科_基数树
《Go ⾼级编程》的 web 部分
Go 夜读 go-micro 分享

